1.What is the Content Negotiation
Simply put, the service provider returns the corresponding message according to the format supported by the client. In Spring, the REST API basically returns in json format. If you need an interface that supports json and other formats, It is obviously unreasonable to develop and maintain multiple sets of codes, and Spring just provides this function, which is ContentNegotiation. In Spring, deciding whether a data is in jso or xml is as follows:
- favorPathExtension suffix pattern, for example: xxx.json, xxx.xml
- favorParameter format mode, for example: xxx?format=json,xxx?format=xml,
- The returned value is determined by the request’s Accept
2.Code Project
Experimental goal: Automatically switch return results in different formats according to different request parameters.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>springboot-demo</artifactId>
<groupId>com.et</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>ContentNegotiation</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>controller
package com.et.contentnegotiation.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, Object> showHelloWorld(){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("msg", "HelloWorld");
return map;
}
}DemoApplication.java
package com.et.contentnegotiation;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}application.yaml
server:
port: 8088
spring:
mvc:
contentnegotiation:
#favor-path-extension: true # header accept
favor-parameter: true # url ?format=xml or format=json
media-types:
json: application/jsonabove it’s just some key codes,for all codes,you can see it in code repository below
Code Repository
3.Test
favorParameter type
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-parameter=truestart spring boot application
http://127.0.0.1:8088/hello?format=xml
http://127.0.0.1:8088/hello?format=jsonreturn multi formats
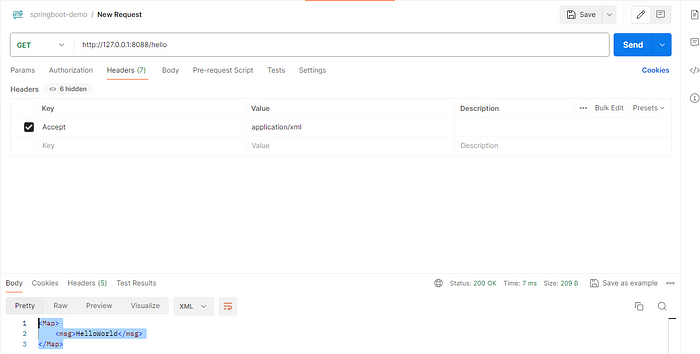
According to Accept
spring.mvc.contentnegotiation.favor-path-extension=trueSet Accept in header: application/xml or application/json